DVWA Tartarus Prerequisites - Blue Team
Note
This will bring up both Red and Blue Team related guests, if you only want Red Team related guests use that version located here.
Video
Conventions
Commands for you to execute are encapsulated in code blocks like this
1
this
The data returned from a command will be represented pictorially like this:
Info looks like this
Tips look like this
Warnings look like this
Danger looks like this
Requirements
To follow along at home for the Blue Team perspective of the DVWA you will need the following:
- Vagrant
- VirtualBox
- Git
- Time
- Windows or Linux host OS
- Some terminal or Powershell awareness
Your host will need the following resources:
Blue team default
RAM: 19 GB
CPU: 11 vCores (~6 physical)
Blue team min
RAM: 13 GB
CPU: 6 vCores (~3 physical)
Small note about the Bluemin setup, the Elastic VM gets deployed with 6GB of RAM, this is against the minimum requirements of 8GB, if you experience instability that could be why.
Installation
The Tartarus Lab located here.
The Nuclei templates are located in the nuclei-templates directory.
Have Vagrant, VirtualBox and Git installed.
In Powershell or the terminal (sh, bash, zsh, fish, etc.):
- Linux
1 2
git clone https://github.com/ScioShield/Tartarus.git cd Tartarus - Windows
1 2
git clone https://github.com/ScioShield/Tartarus.git cd Tartarus
Once the Tartarus Lab has been downloaded you can now bring up the machines with:
- Linux
1
export VAGRANT_VAGRANTFILE=Vagrantfile; vagrant up opnsense
Then run:
1
HOSTS=dvwa vagrant up opnsense elastic dvwa kali
- Windows
1
$env:VAGRANT_VAGRANTFILE = "Vagrantfile"; $env:HOSTS = "dvwa"; vagrant up opnsense
Then run:
1
vagrant up opnsense elastic dvwa kali
As documented here in the readme, there is the min option to deploy with only 13 GB RAM and 6 vCores.
Expected terminal results (trimmed for convenience):
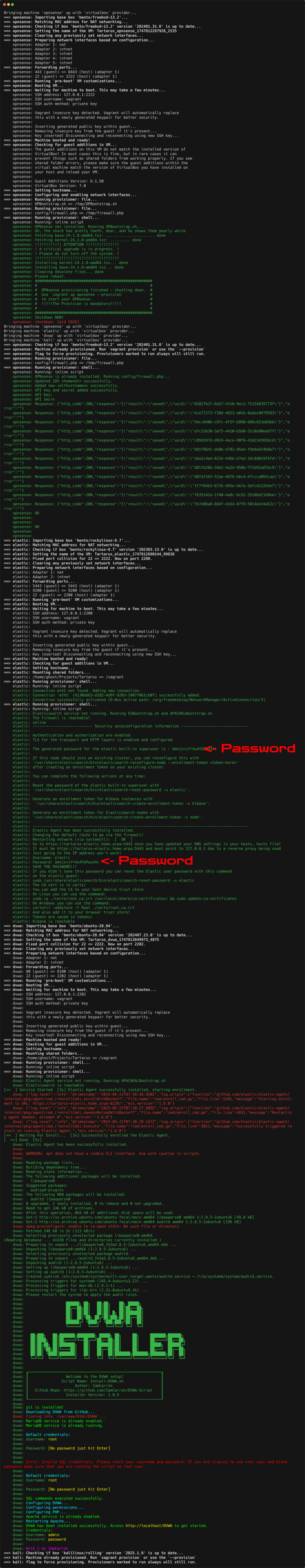 Output of bringing the hosts up with vagrant on Linux
Output of bringing the hosts up with vagrant on Linux
As seen above the Elastic password gets printed to the screen in the final section of bringing up the elastic host, if you didn’t catch it you can do a little:
1
2
vagrant ssh elastic
sudo /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic
This resets the password to another random value.
If you are in are not in the UTC timezone you will need to update the timezones of all the hosts to where you are with the command:
For the Opnsense node it’s in the GUI System->Settings->General should be a setting on that page.
Also don’t forget to restart the Lab once the timezone has been set.
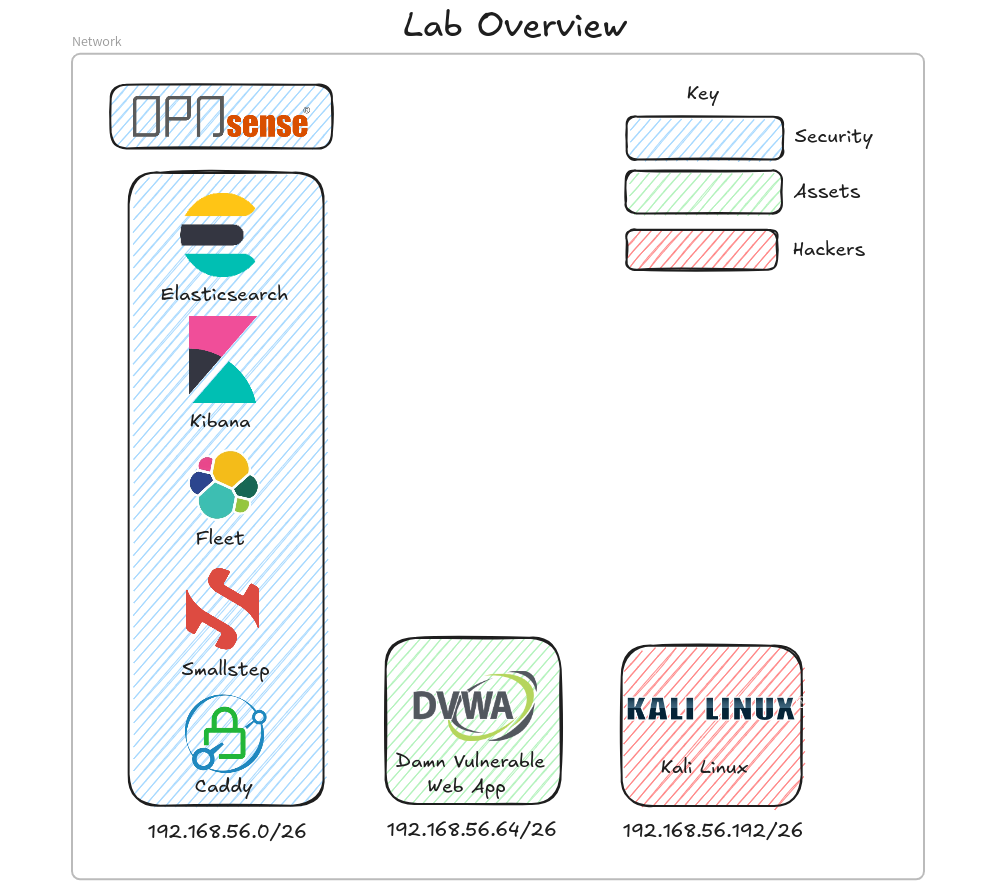
Architecture
For this lab we only have Blue team related guests, Opnsense, DVWA, and Kali. The Opnsense node is required to facilitate network connectivity between guests.
Opnsense
You can log into the Opnsense firewall by going to https://tartarus-opnsense.home.arpa:8443/ once you’ve updated your hosts host file to point tartarus-opnsense.home.arpa to 127.0.0.1.
Username: root
Password: opnsense
To maintain network segregation we use an Opnsense firewall. The firewall acts as a stateful firewall, DNS, DHCP, and NTP server. We use a class C network the “192.168.56/24” that we subdivide into 4 /26 networks, so with the WAN network we have LAN (or Security in the above diagram), Assets, Targets, and Hackers.
mindmap
root((Firewall Rules))
LAN
Allow
ANY
ANY
ANY
WAN
Allow
TCP
HTTPS
self
SSH
self
Assets
Allow
UDP
NTP
self
DNS
self
TCP
Elasticsearch
LAN
Web Traffic
ANY
Block
ANY
ANY
RFC1918
Targets
Allow
TCP
Elasticsearch
LAN
Block
ANY
ANY
RFC1918
Hackers
Allow
UDP
DNS
self
NTP
self
TCP
Web Traffic
ANY
SSH
Assets
A mind map representation of the firewall rules.
Elastic SIEM
You can log into the Elastic instance by going to https://tartarus-elastic.home.arpa:5443/ once you’ve updated your hosts host file to point tartarus-elastic.home.arpa to 127.0.0.1.
username: elastic
password: (In the terminal you ran vagrant up from)
A hint you can add the root CA to your browser trust store, this will prevent those pesky “This site is unsafe blah blah”. It’s one of the benefits of the project rolling it’s own root certificate authority, thanks to SmallStep. The cert even survives vagrant destroy :)
Damn Vulnerable Web Application
The many blog posts on the DVWA makes it a prime target to demonstrate the Tartarus playground. All the supporting infrastructure allows for a near plug-and-play solution, the only modifications needed are to add the Apache Web server integration, install the Elastic Agent, and install the DVWA on a Debian based distro in this case Ubuntu.
 Example DVWA login page from Kali.
Example DVWA login page from Kali.
Kali
The only guest in the Hackers network, this guest is the beach head into the rest of the network. You can customize the base image to your harts content, or just destroy it and start fresh every time.
username: vagrant
password: vagrant